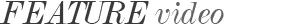Orbital Procedures
| Blow-Out Fractures | 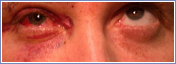 |
The eye is protected by a pear-shaped bony orbit. When an object, larger than the size of the orbital entrance, hits the eye (but does not penetrate) it creates a sudden rise in pressure within the orbit and may result in a ‘blow-out fracture’.
The orbital floor is the most susceptible to this type of fracture.
| Orbital Tumours | 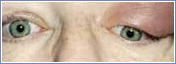 |
The orbit is the area containing the bones of the eye socket, the eye ball, eye muscles, optic nerve and fat filling the spaces in between. A tumour may occur in any of these sites. Tumours may also arise from the surrounding sinuses, brain and nasal cavity. These tumours may grow through bone and invade the orbit.
Orbital tumours affect people of all ages and are usually benign.
| Thyroid Eye Disease |  |
Grave’s Disease, also referred to as Thyroid Eye Disease (TED), is an autoimmune disease which involves both the orbital tissues and the thyroid gland.
| Anophthalmos | 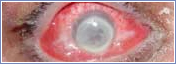 |
Anophthalmos is the term used for the loss of one eye. When surgery is performed to remove an eye the operation is called an ‘enucleation’.